RESEARCH TOPICSRESEARCH TOPICS
Reduction of Greenhouse Gases
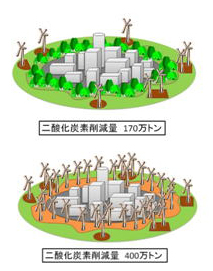
"Effect of Renewable Energy Introduction and Residents' Acceptance"
It is expected that many excess land areas are produced by the falling
birthrate and the aging population. Then, how can we utilize the areas?
One possible idea is installation of new energies. For example, how about
installing solar energy panels there? We can reduce much GHGs! However,the
city covered with solar panels may not be comfortable for people. It is
expected that too artificial landscape can decrease the amenity. In our
lab., we have tried to evaluate the relationships between GHGs reduction
and people’s acceptance of new energies like solar panels and wind mills.
We show various figures consisted of greens and new energies as well as
GHGs reduction potentials, and evaluate the people’s preferences through
the questionnaire survey.
"Evaluation of environmental aspects of various systems using Life Cycle Assessment"
To evaluate various measures from the environmental viewpoint, we use Life
Cycle Assessment (LCA) to estimate all environmental loadings deriven from
each measure. For evaluating some policies and systems specific to the
target region, we try to collect local data through statistics, literatures,
and interviews. Currently we use LCA approach to evaluate prefabric construction
in Thailand and de-centralized wastewater treatment systems in rural areas
in China.
Waste Management

"Evaluation of Biofuels using Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)"
Production of bio-fuels like bio-ethanol and biodiesel has raised various
controversies. There are doubts whether bio-fuel production can contribute
to GHGs reduction when all life cycle processes like fertilizer production
and electricity use are involved in the estimation of GHGs emission. The
social effects such as competition with food production and land use change
are also considered to be important aspects relating to bio-fuels. Our
lab. has tried to estimate true CO2 reduction using LCA approach and evaluate
social effects driven by bio-fuel production.
Recent target fields and materials: Brazil (sugar cane), India (jatropha),
Indonesia (palm), Thailand (waterhyacinth)

"Strategy for Utilization of Organic Wastes"
"Biomass" has been intensively used because of its "Carbon
Neutral" feature. It is believed that biomass use can achieve CO2
reduction, however, there still remains controversial aspects. For preventing
the competition with food production and promoting the effective biomass
use, the utilization of untapped biomass like organic wastes is preferable.
At the same time, appropriate waste management in urban area should be
considered.
We have dealt with rice husks in Viet Nam and water hyacinth in Thailand
etc. Those organic materials derive water and air pollution in the regions.
If we can show effective use of them, it can contribute not only to GHGs
reduction but also to local environment improvement. We conduct LCA, cost
evaluation and social surveys and evaluate the strategies.
Environmental education/ Fostering Environmental Behaviors
It is necessary to understand the people's perception and consciosness for making effective environmental measures. We take into account the residen's view and try to build-up environment-friendly society. We try to grasp people's preferences through the questionnaires. Beside, we focus on the effect of information. For example, if we offer the CO2 data based on Life Cycle Assessment, is it effectife to push pro-environment behavior? How and what data should be given to the people to enforce their pro-environmental behaviors? To answer these questions, we are currently conducting the below studies.
"Factors influencing on Household Pro-environment Behaviors"
To build-up more effective measures for encouraging citizens to behave
environmentally, the current citizen’s state should be well comprehended.
Some studies have evaluated the environmental burden of each behavior,
but little attention has been given to the citizen itself as the performer
of daily life. In this study, we extracted 44 everyday-behaviors and 13
machinery-introductions and a questionnaire to ask environmental consciousness,
practice degrees of behaviors and the reasons, and the perceived effectiveness
of those behaviors is conducted. Through the surveys, we try to reveal
the relationships between the people's behaviors nad other factors like
social conditions, psychological perceptions, socio-demographics, etc.
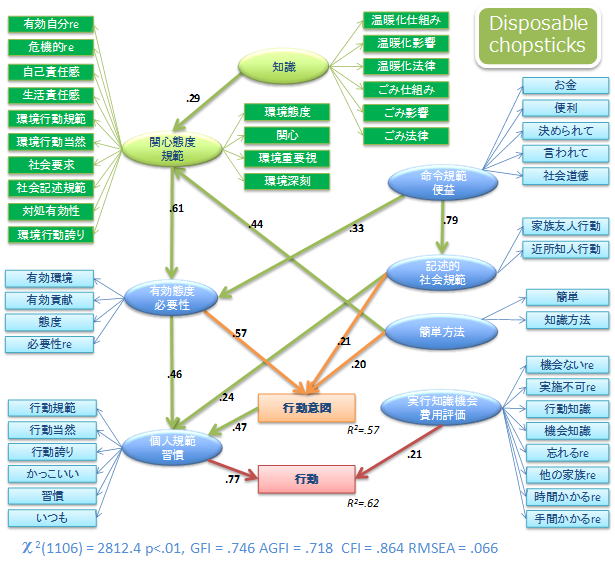
Psychological modeling for pro-environmental behaviors
"Education involving Life Cycle Thinking"
It is quite important to develop discipline of Life Cycle Thinking (LCT)
in elementary education. We try to develop educational frameworks, materials,
and LCA database for glowing LCT especially in the house science, which
is highly related to our daily lives. Besides, LCA data base of daily behaviors
can be also used for adults' education through application of smartphone,
etc.
・Evaluation of Users'(consumers & tool developers)demands
・Text analysis of environment-related contents in the house science textbooks(below
figure)
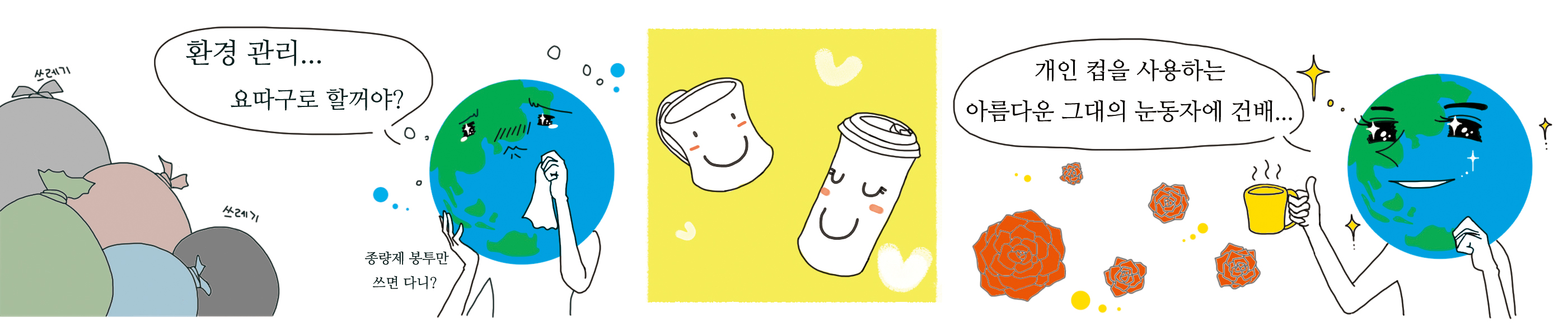
"Information effect on Intentions and Actual Environmental Behaviors"
In the case when lacking information is barrier of a behavior, giving information
can work effectively to foster the citizen's behavior. In this study, we
investigate what information can increase people's intentions on environmental
behaviors. Residents' perceptions of each information is investigated by
means of questionnaire survey. Finally, the effective information provision
ways are analyzed through the actual campaigns (Below picture is part of
our trial in the Seoul free-paper)

QOL: Quolity of Life
"Relationships between Urban forms and QOL"
Measures of "Compact City"or new transportation facilities have
posibility to reduce environmental loadings. However, in urban lives, we
should consider not only environmental burdens but also quality of life
(QOL).
We evaluate environmental loadings and people's objective and subjective
satisfactions on various aspects of QOL.
River basin management
"Prediction and Adaptation of Flood increase derived by Climate Change"
Hat Yai area was strongly damaged by flood in 2000. They also had several
big flood disasters besides it. Under future climate change, flood events
can increase.
In this study, we predict future flood increase using GCM & downscaling
and hydrological model. And taking into account land-use change and hard
or soft infra installation, various measures for flooding are evaluated.
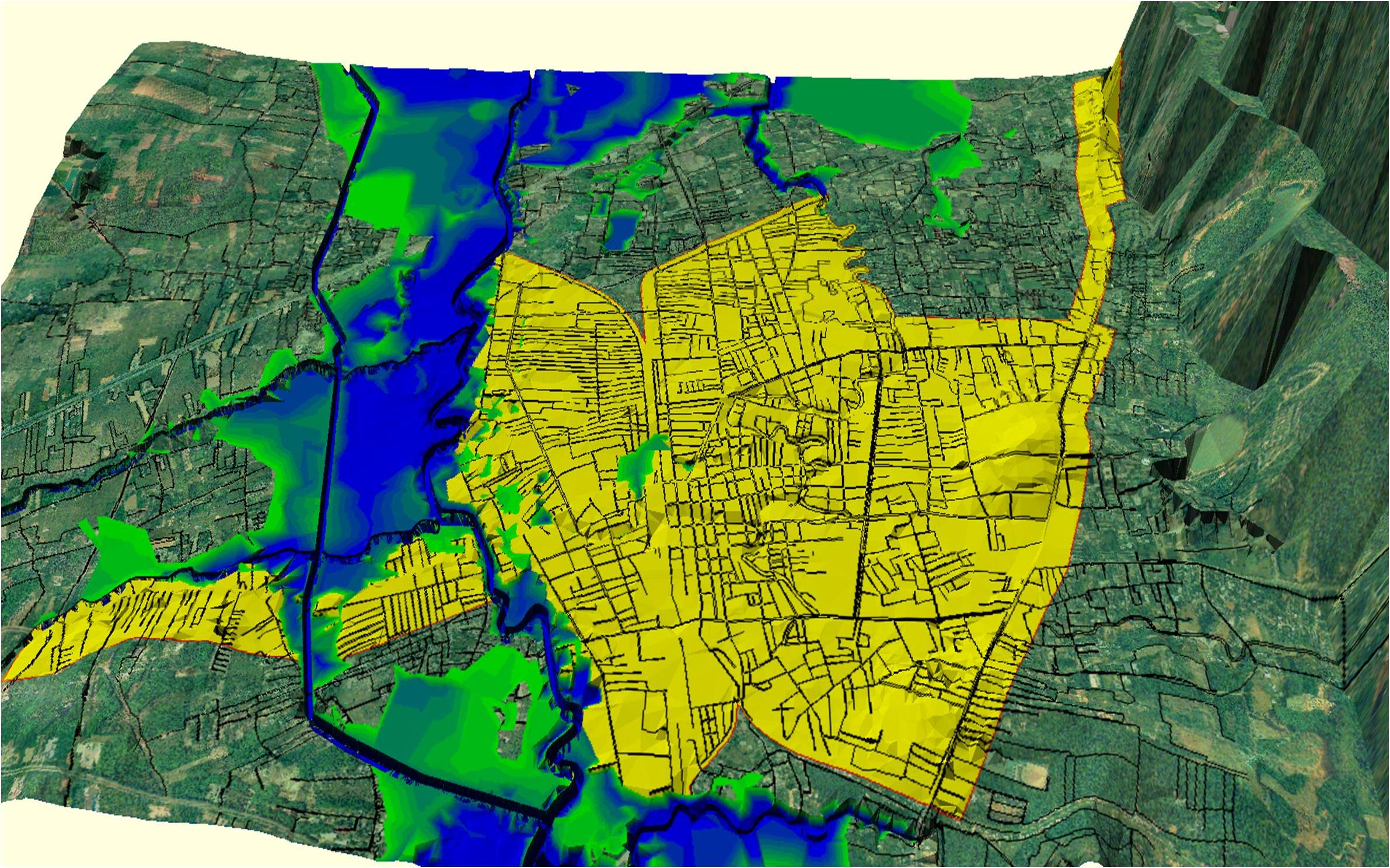
Flood projection in Hayai, Thailand
"Multi-objective Optimisation of Reconstruction of Water Systems"
When we re-construct water systems, various aspects such as lifecycle and
local environmental impacts, cost, and impact on water cycle, should be
considered. Instead of integration of these aspects, we apply multi-objective
optimisation. Through the optimisation, we can get multiple optimized solutions
which can meet various people's preferences.
Value for Waterfronts
"Valuation structure for Urban Rivers"
 River fronts are important amenity spaces in urban areas. However, perceptions
on rivers vary from person to person. For conductiong cost-benefit analysis,
value and valuation structure of water-front must be revealed.
River fronts are important amenity spaces in urban areas. However, perceptions
on rivers vary from person to person. For conductiong cost-benefit analysis,
value and valuation structure of water-front must be revealed.
We try to quantitatively evaluate the valuation structure using online
questionnaire, conjoint analysis, structural equation modeling, latent
class analysis, etc.
"Water Quality Improvement of Edo-castle Moat"
Castle moats are important urban water-fronts. However, many moats are
closed water bodies and the water quality is not so good. The moat of Edo
castle receives water only from rain and CSO (combined sewer outflow) and
the water quality is also bad (right photo shows severe algal bloom in
summer). In urban areas, reclaimed water can be one of the most stable
water sources. We evaluate the effects of introduction of reclaimed water
on the water quality of the moat and also evaluate the cost and people's
impressions.
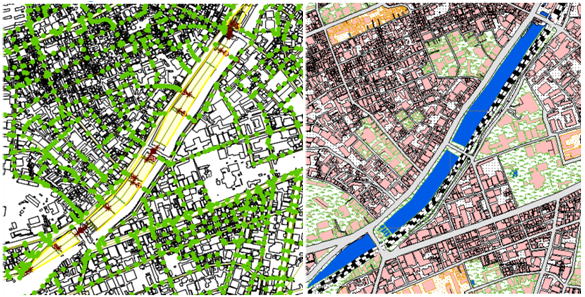
Simulation of CSO amounts using Infoworks & GIS
Risk Communication

"Risk Perceptions and Communications on Drinking Water"
Many cases where big gap exists between the specialists and citizens have
been observed. We pick up "Risk Communication" as typical
communication between specialists and citizens, and investigate how to
transfer the information of risk derived from microorganisms or chemicals.
For reducing the gap between the specialists and citizens about risk perception
of drinking water, appropriate risk communication has been thought to be
necessary.
However, a question comes up: what is the appropriate communication like?
Is it true that provision of information is enough for the communication?
To know the effect of information on the citizen’s risk perception, we
applied on-line questionnaire survey and evaluated the effects of provided
information. The respondents were divided into various groups and the combination
of provided information was changed for each group.The risk perception
was asked using the scales proposed by Slovic (1987), where the extraction
of two factors such as “dread factor” and “unknown factor” was expected.
Besides, the questions for the risk acceptance and risk orientation were
asked to analyze the respondent’s personality.。